| Strain Name |
|
Common Name |
B-NDG B2m KO mice plus |
| Background | B-NDG | Catalog number | 110601 |
|
Related Genes |
B2m (beta-2 microglobulin) ; |
||
|
NCBI Gene ID |
12010,14132 | ||
Mice Description
Human PBMC-engrafted humanized mice are attractive models for in vivo analysis of human immune responses. We previously reported that human PBMCs could be engrafted in B-NDG mice successfully. However, because of severe xenogeneic graft versus host disease (xeno-GVHD) in these mice, there is a limited window for experiments. The onset of GvHD is directly related to the degree of engraftment of human T cells. The mismatches between human and mouse MHCs are the main cause of GvHD after human PBMC transplantation1. Data have shown that knockout of MHC class I and/or II molecules in mice attenuates GvHD and prolongs the window period for experiments after human PBMC transplantation.
MHC class I molecules consist of two subunits, α and β chains. The B2m (beta-2-microglobulin) gene encodes the β chain. Knockout of the B2m gene in mice can result in the inability to form intact MHC class I molecules and cannot be expressed on the cell surface to exert antigen presentation, thereby alleviating GvHD. However, B2M is also a subunit of FcRn, the Fc receptor for IgG. The structure of FcRn is similar to that of MHC class I molecules, consisting of the α chain encoded by the Fcgrt gene and the β chain encoded by the B2m gene. FcRn can bind to antibodies and prolong the half-life of antibodies. Loss of B2M expression results in a shortened half-life of the antibody in mice.
Biocytogen developed the B-NDG B2m KO plus mice, which knocked out the mouse B2m gene, while the mouse B2m and Fcrgt fusion gene were knocked in at the mouse Fcgrt gene locus. This mouse has a background of B-NDG mice and does not express MHC class I molecules on the cell surface. Compared with B-NDG mice, this mouse has no difference in the metabolism of IgG and is effective in delaying the development of GvHD. This model can be used to investigate the in vivo mechanism of xenogeneic graft versus host disease (GvHD) and to evaluate the efficacy of antitumor drugs using humanized mice reconstituted with human PBMCs.
Expression analysis of MHC class l molecules
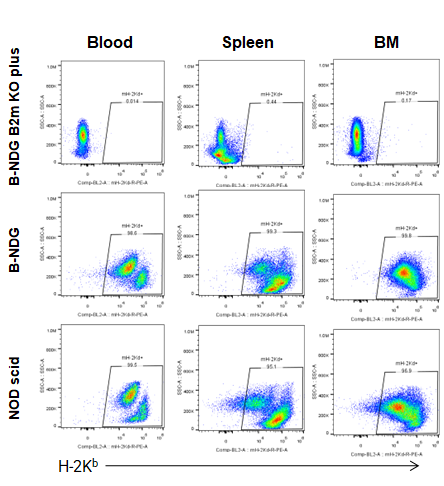
Expression of MHC class I in B-NDG B2m KO plus mice
Blood cells, splenocytes, bone marrow cells were respectively collected from B-NDG B2m KO plus mice, B-NDG mice, NOD scid mice (n=5). Expression of MHC class I (H-2Kb) was analyzed with FACS. Results showed that MHC class I molecule was detectable in B-NDG mice and NOD scid mice. But there was no MHC class I molecule detectable in B-NDG B2m KO plus mice.
Expression analysis of MHC class II molecules
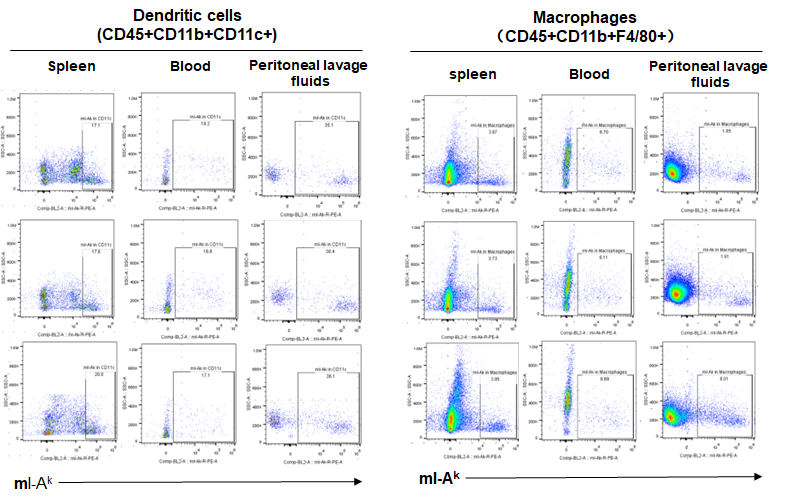
Expression of MHC class II in B-NDG B2m KO plus mice
Blood cells, splenocytes, bone marrow cells were respectively collected from B-NDG B2m KO plus mice, B-NDG mice, NOD scid mice (n=3). Expression of MHC class II (I-AK) was analyzed with FACS. Results showed that the MHC class II molecules were all detectable in dendritic cells and macrophages of the three strains of mice.
Flow cytometric analysis of T , B and NK cells

Blood cells, splenocyte, cells were collected from B-NDG B2m KO plus, B-NDG, NOD-scid and C57BL/6 mice (n=5) and analyzed by flow cytometry with T, B and NK cells. T, B and NK cells were not detectable in B-NDG B2m KO plus and B-NDG mice. T, B cells were undetectable and NK cells were detectable in NOD scid mice. T, B and NK cells were detectable in C57BL/6 mice.
Flow cytometric analysis of Macrophages
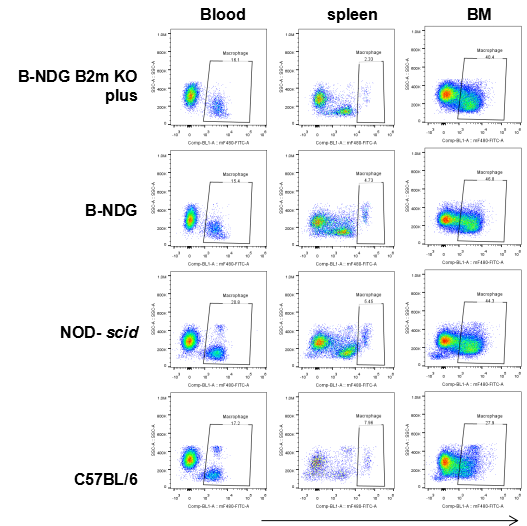
Blood cells, splenocyte, Bone marrow cells were collected from B-NDG B2m KO plus, B-NDG, NOD-scid and C57BL/6 mice (n=5) and analyzed by flow cytometry with Macrophages(mCD45+mCD11b+mF4-80+). Macrophages were detectable in B-NDG B2m KO plus, B-NDG, NOD-scid and C57BL/6 mice.
Flow cytometric analysis of DC cells and monocytes
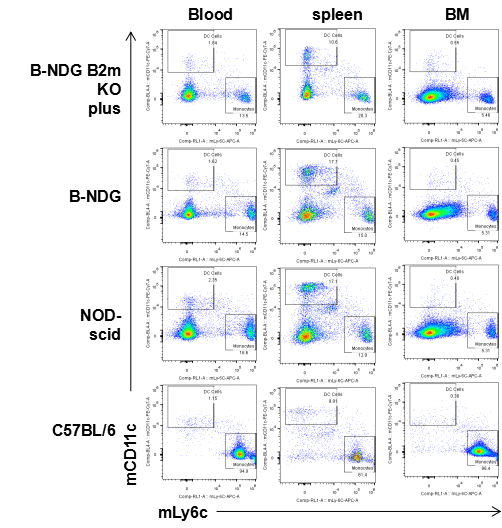
Blood cells, splenocyte, Bone marrow cells were collected from B-NDG B2m KO plus, B-NDG, NOD-scid and C57BL/6 mice (n=5) and analyzed by flow cytometry with DC cells (mCD45+mCD11b+mCD11c) and monocytes (mCD45+mCD11b+mLy6c). DC cells and monocytes were detectable in B-NDG B2m KO plus, B-NDG, NOD-scid and C57BL/6 mice.
Histopathological sections of tissues from B-NDG B2m KO mice plus and control mice

Histopathological sections of tissues from B-NDG B2m KO mice plus and control mice.
(A) Spleen from C57BL/6 has normal structure with well-defined follicles. (B) Spleen from NOD-scid show hypoplasia of white pulp. (C, D) Spleen from both B-NDG and B-NDG B2m KO mice plus show complete loss of follicular structure. (E) Thymic lobes from C57BL/6 have normal structure with a well-defined cortex. (F) Thymic lobes from NOD-scid mice are hypoplastic and lack a defined cortex.(g) Thymic lobes from B-NDG mice are severely hypoplastic and lack a defined cortex. (H) B-NDG B2m KO mice plus show no thymic lobes on the normal anatomy location.
PK analysis of human IgG in serum
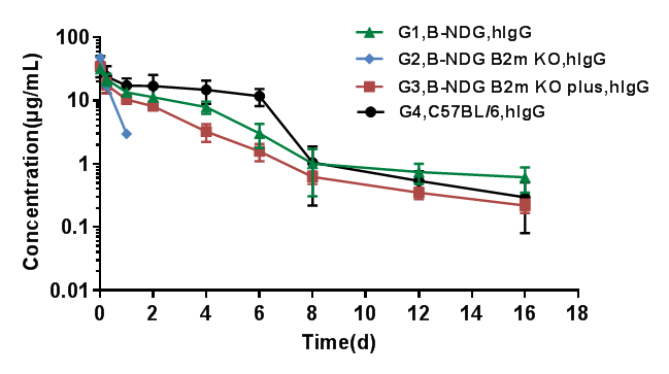
The PK of human IgG in B-NDG B2m KO mice plus was similar to that in wild-type mice.
B-NDG, B-NDG B2m KO mice, B-NDG B2m KO mice plus and C57BL/6 mice were treated with human IgG (n=5). Blood samples were collected at different time point for the PK assay. Results showed that the PK of B-NDG mice and B-NDG B2m KO mice plus groups were basically in line with the pharmacokinetic characteristics, with no difference compared with wild-type C57BL/6 mice, and the drug concentration of B-NDG B2m KO mice group could not be measured at the time point 2 days later.
Effectively delayed the onset of GvHD induced by human PBMC engraftment
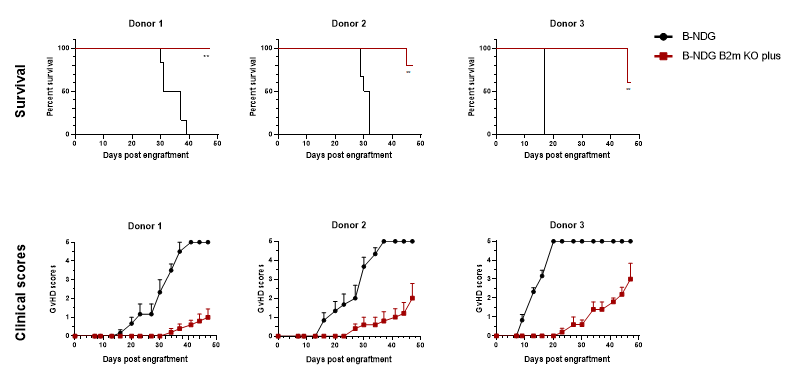
B-NDG B2m KO mice plus can effectively delay the onset and reduce the severity of GvHD induced by human PBMC engraftment.
B-NDG B2m KO plus mice (n = 5, female, 11-week-old) and B-NDG mice (n = 6, female, 10-week-old) were injected intravenously with human PBMCs (2E7) from three healthy donors on day 0, and each mouse was scored twice weekly for clinical signs according to GvHD scoring criteria. The results showed that B-NDG B2m KO plus mice could significantly prolong the survival time, delay the occurrence and reduce the severity of GvHD compared with B-NDG mice in the GvHD model constructed after human PBMC transplantation.
B-NDG B2m KO mice plus are well suited for human immune system engraftment

B-NDG B2m KO mice plus are well suited for human immune system engraftment.
Human PBMC (5E6) were intravenous implanted into homozygote B-NDG B2m KO mice plus and B-NDG mice (female, 7-week-old, n=6). Representative flow cytometric analysis of PBMCs from mice after engraftment with human PBMC.B-NDG B2m KO mice plus show a little change in body weight and exhibit longer survival compared with B-NDG. The result showed that human PBMC engrafted humanized mice model was successfully constructed.
Anti-tumor efficacy in PBMC RKO model in B-NDG B2m KO mice plus
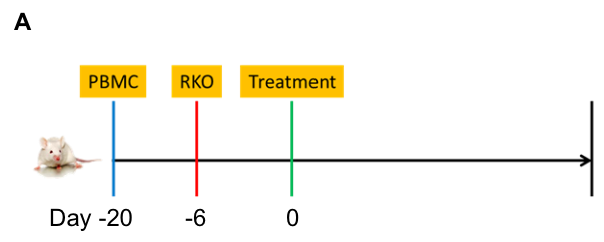
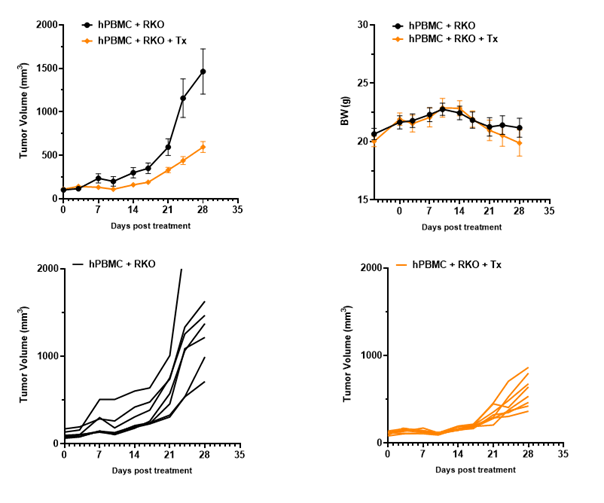
Antitumor activity of the combination of pembrolizumab (anti PD-1) and ipilimumab (anti CTLA4) in B-NDG B2m KO mice plus reconstituted with hPBMCs.
Human colon cancer RKO cells (5E6) were subcutaneously implanted after human PBMCs (1E7) injected into B-NDG B2m KO mice plus (n=7/8). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 100-150 mm3. Anti-human PD-1 antibody and anti-human CTLA4 antibody (in house) were injected intraperitoneally. The results showed that combination of anti-hPD-1 antibody and anti-CTLA4 antibody can effectively inhibited the tumor growth, indicating that B-NDG B2m mice plus reconstituted with PBMCs provides a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
In vivo efficacy of CAR-T can be effectively evaluated in B-NDG B2m KO mice plus
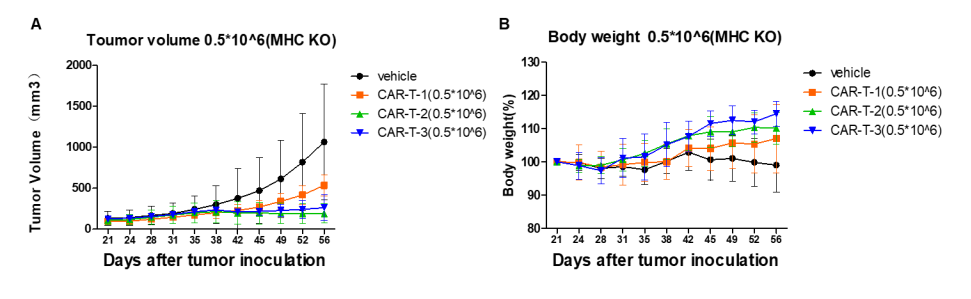
A human lung cancer model was established by implanting NCI-H226 into B-NDG B2m KO plus mice, which can effectively evaluate the in vivo efficacy of CAR-T therapy.
Human lung cancer cells NCI-H226 (1E7) were implanted into B-NDG B2m KO mice plus. Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 150±50 mm3, at which time they were treated with CAR-T cells (5E5) with schedules indicated in panel. (A) Tumor volume. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. The results showed that CAR-T cells differently inhibited tumor growth in B-NDG B2m KO mice plus. Within 5 weeks of CAR-T treatment, the body weight of mice in the treatment groups continued to increase without significant GvHD.
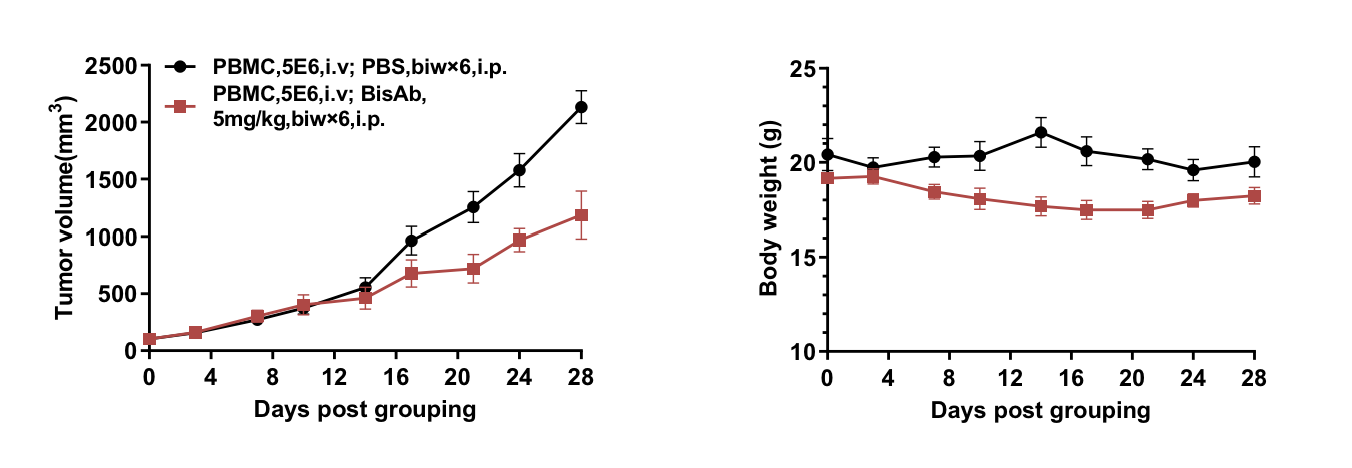
Bispecific antibody in vivo efficacy evaluation in B-NDG B2m mice plus reconstituted with human PBMCs
Summary
- Flow cytometric analysis of MHC class l and Il expression. MHC class I were not detectable in B-NDG B2m KO mice plus .
- Flow cytometric analysis using specific markers for T, B and NK cells. T, B and NK cells were not detectable in B-NDG B2m KO plus.
- Determination of plasma concentrations of human IgG in different mice .The results showed that the PK results of B-NDG and B-NDG B2m KO mice plus groups were basically in line with the pharmacokinetic characteristics, with no difference compared with wild-type mice Physiological function
- B-NDG B2m KO mice plus are well suited for human immune system engraftment. Human PBMC (5E6) were intravenous implanted into homozygote B-NDG B2m KO mice plus and B-NDG mice (female, 7-week-old, n=6). Representative flow cytometric analysis of PBMCs from mice after engraftment with human PBMC. B-NDG B2m KO mice plus show a little change in body weight and exhibit longer survival compared with B-NDG.











